Brazil is well-placed to weather a trade war as a top exporter of vital commodities with strong links to the world’s big three economic blocs, said finance minister Fernando Haddad.
“Brazil is in a privileged situation,” he told the Financial Times in an interview ahead of a trip to Europe. Haddad said he had high hopes for a free trade deal agreed between the EU and South American countries, while also boasting of an “excellent bilateral relationship” with China and calling the US “a historic partner”.
Haddad, a former academic and longtime ally of veteran leftwing President Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva, was chosen to oversee Latin America’s largest economy when Lula returned to power in 2023.
There was “no way”, he said, that Brazil would pick a side between China and the US, its first and second-largest trading partners.
But it would also aim to open to new markets, he said, noting that Lula “worked very hard personally” to seal the Mercosur trade grouping’s blockbuster deal with Europe, which was signed in December after more than 20 years of negotiation but is still awaiting ratification.
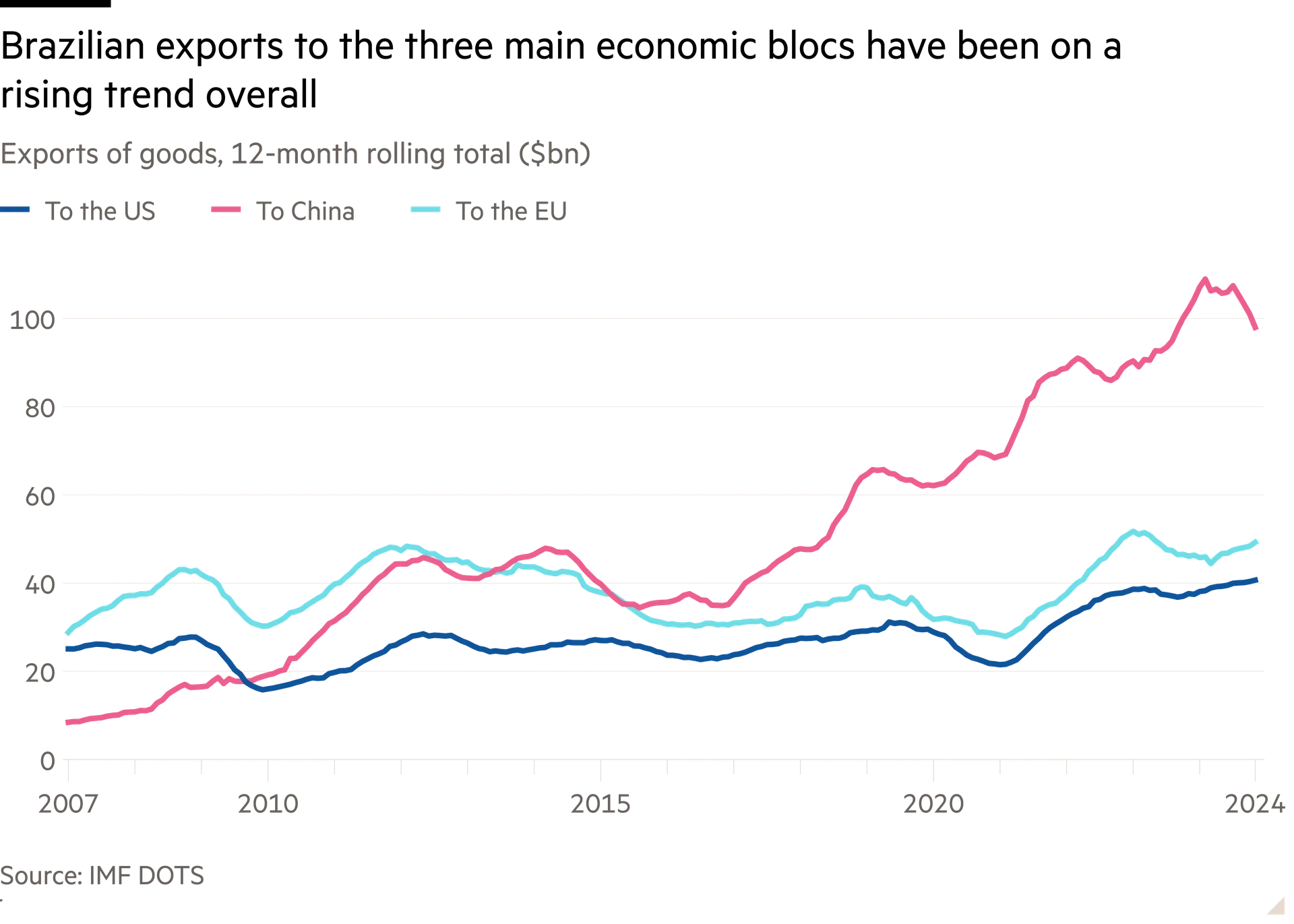
The accord between the EU and the Mercosur bloc — which comprises Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Paraguay and Uruguay — eliminates tariffs on 90 per cent of bilateral trade, but must overcome resistance from some EU member states, including France and Poland.
“I really believe its time has come, as I believe that Europe realises it also has no other path,” Haddad said. “This is not about moving away from China, from the United States . . . but we have to create new spaces.”
Brazil is one of the world’s top food exporters, and Haddad underlined the growing importance of its processing industry. “Brazil is no longer just the granary of the world. Brazil is transforming itself in part into a kind of supermarket of the world,” he said.
The White House has named Brazil among nations charging high duties on US products, but it has not yet been hit with targeted measures and President Donald Trump has barely mentioned the country since taking office for the second time.
Lula has been careful to avoid open conflict with Washington, though he vowed to complain to the World Trade Organization about Trump’s 25 per cent tariff on all steel imports.
Trump is looking to reverse US trade deficits with other countries, but Haddad pointed out Brazil is one of the few major economies with whom Washington enjoys a surplus in goods, which hit $7.4bn in 2024.
He also insisted Brazil’s effective import duties on US wares were far lower than headline figures because of exemptions for specific products.
Haddad arrives in France on Monday and was optimistic about Brazil’s trade relations with its partners on the continent. “Especially since recent episodes that suggest Europe is back in the game and will try to react to being walled in by cultivating multilateralism,” he said.
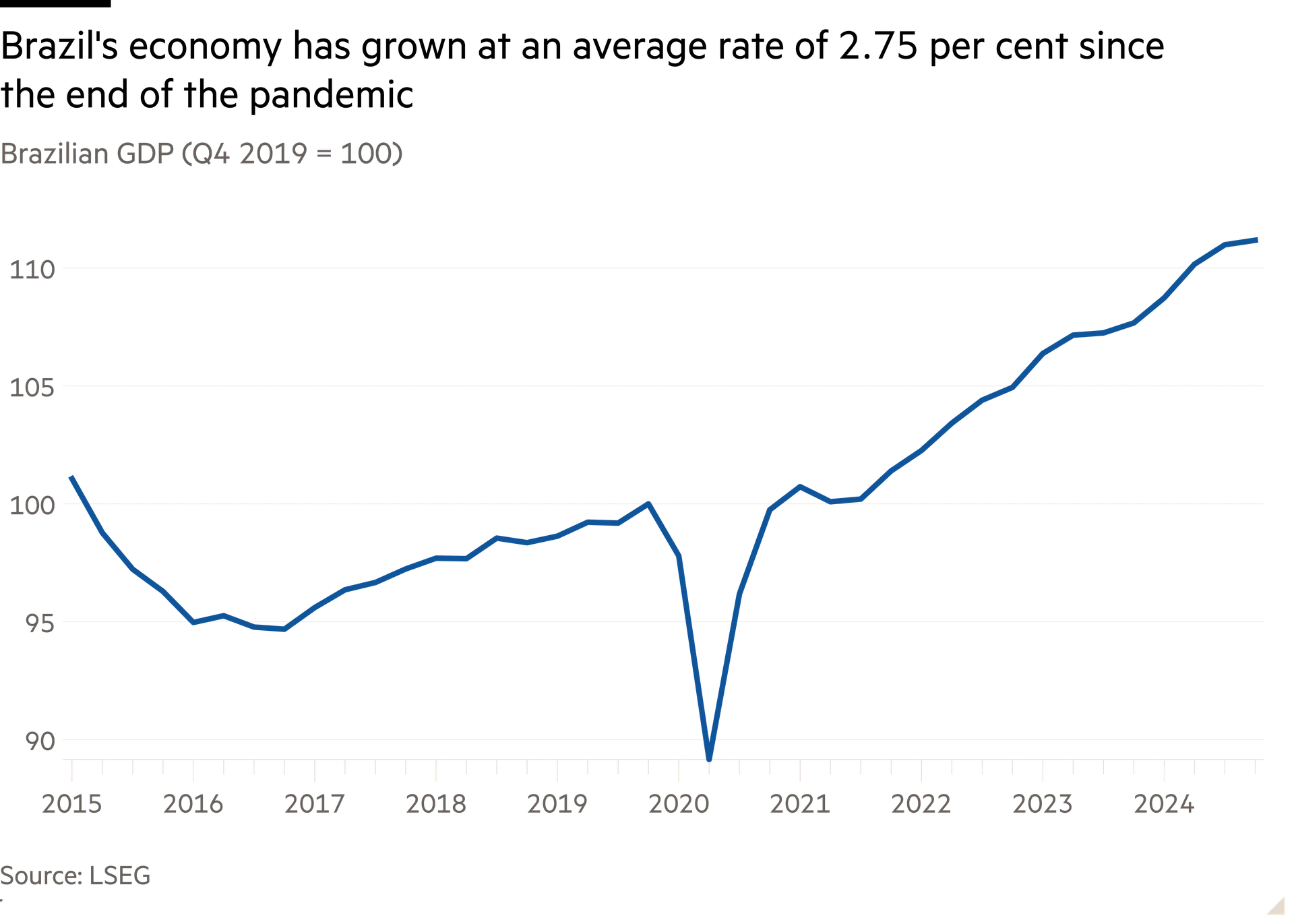
At home, Haddad has overseen stronger-than-forecast GDP growth, low unemployment and a historic reform to simplify Brazil’s notoriously complex tax system. But he is under pressure from the business class over the fragile public finances and from leftwing members of his own party, who resist spending cuts.
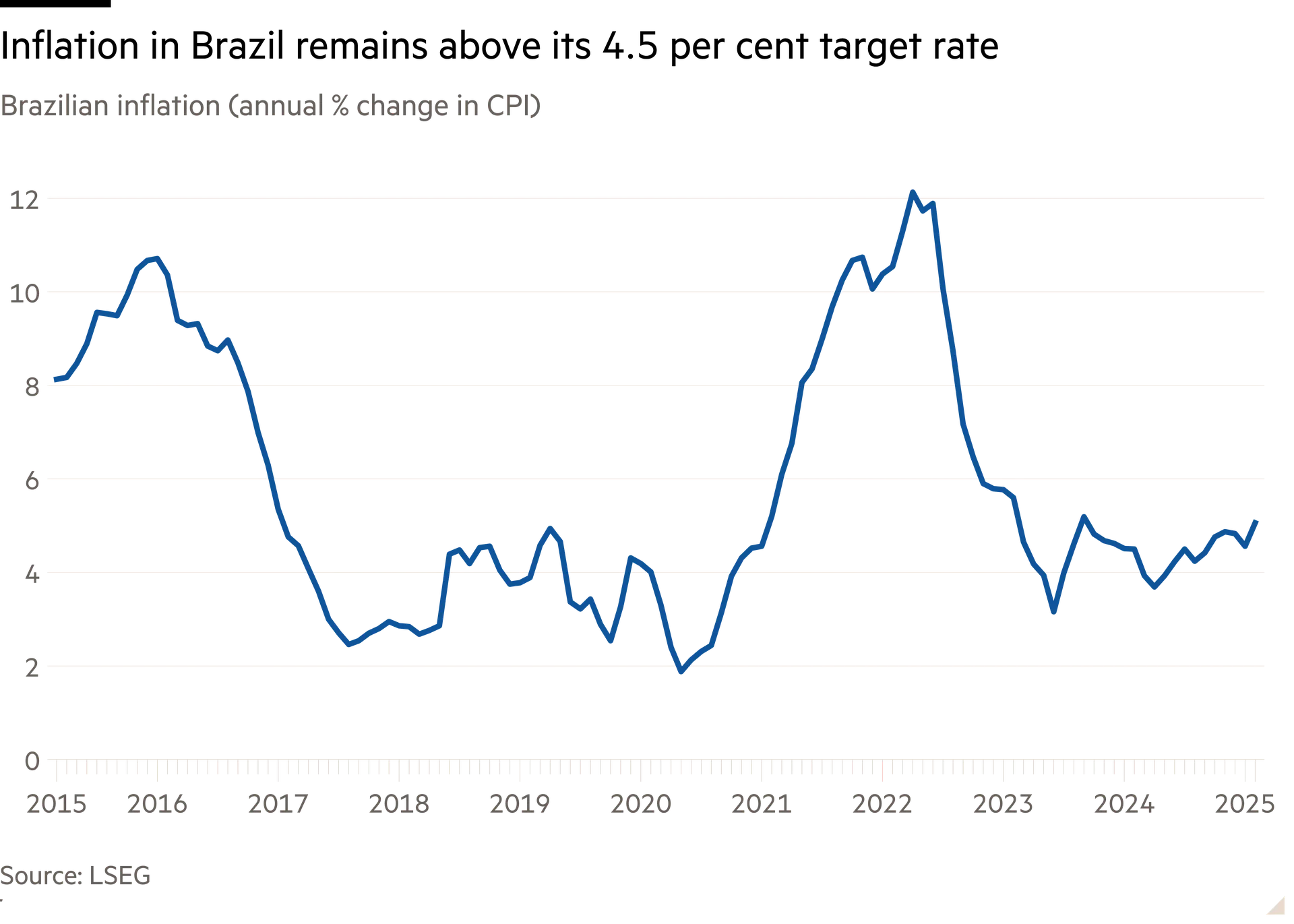
Investor concerns over the high nominal budget deficit — running at 8 per cent of GDP in the year to January — and debt triggered a fall in Brazil’s currency in 2024, while Lula’s popularity has been hurt by inflation which is overshooting a target ceiling of 4.5 per cent.
Critics say excessive government spending is complicating the task of the central bank, which has raised interest rates to 14.25 per cent.
Haddad said the financial sector had been excessively pessimistic since Lula’s election victory. Some asset managers who bet against the government had “lost money,” he said. “They’re upset the government worked out.”
He insisted he had been tough on spending, cutting R$35bn ($6.1bn) from the budget last year, and said the government was continuing to straighten out public finances. IMF forecasts, however, show Brazil’s gross government debt rising from 87.6 per cent of GDP last year to 97.6 per cent in 2029.
Asked whether the government had the fiscal deficit under control, he replied that this was a question which made no sense. “The finance minister is like a guy in a Formula 1 cockpit in the middle of a race . . . you don’t call him and ask whether everything is under control.”
“I think we have a good team, a good car and, who knows, maybe even a good driver.”
Data visualisation by Keith Fray