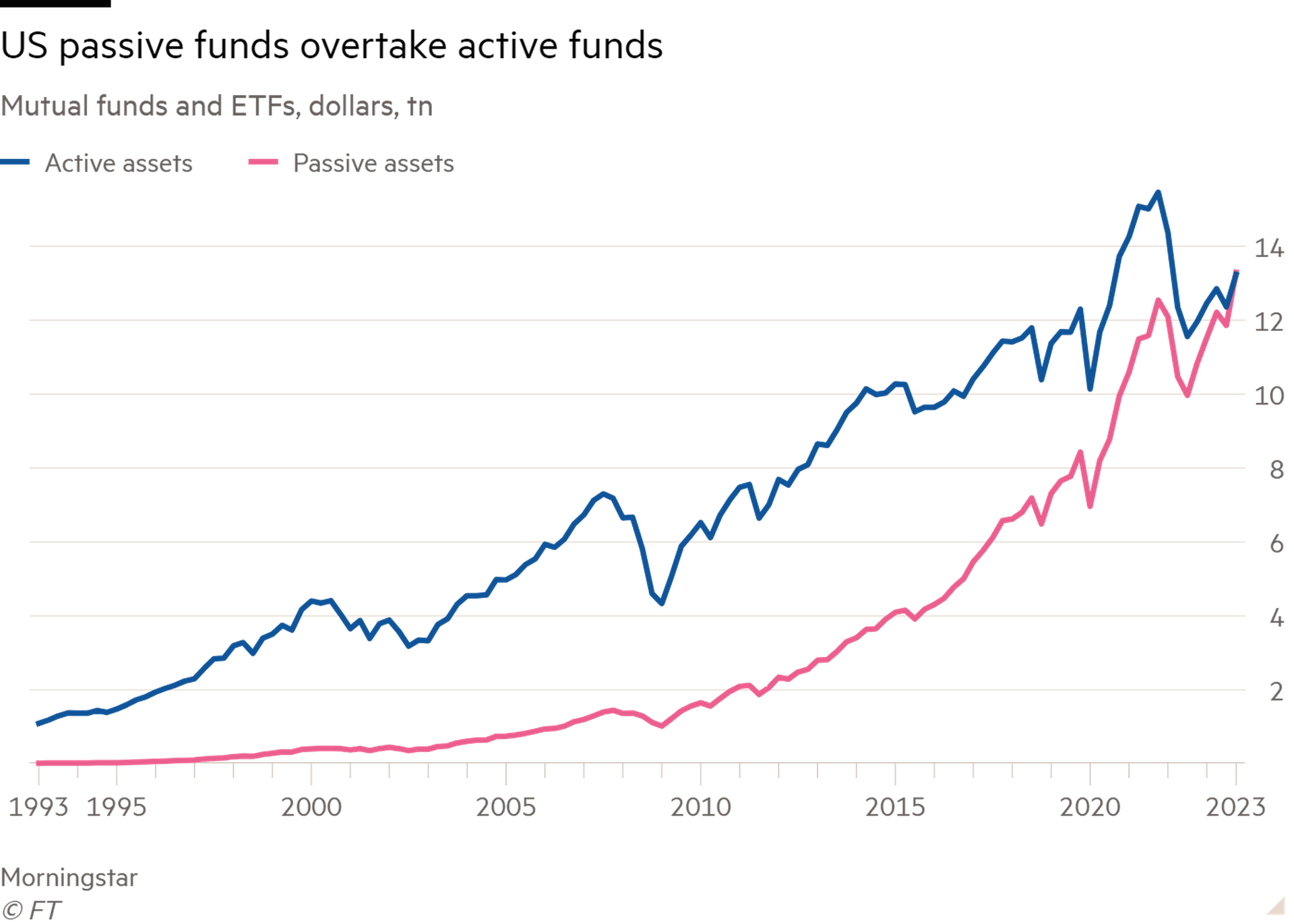
“Don’t look for the needle in the haystack. Just buy the haystack,” wrote John Bogle, the late founder of investment firm Vanguard. His quip is now conventional wisdom. America’s passively managed mutual funds and exchange traded funds — which mimic overall market indices — ended last year with more assets than active ones, following years of strong inflows.
Though many still tout their stock and bond picking credentials, active fund managers only rarely generate alpha (or market-beating returns). In the long term the index tends to win, substantiating Bogle’s advice. So, why risk money hoping to unearth the next Google or Amazon when it is both safer and more lucrative to be invested in everything?
That is the question active fund managers fear too many investors are now asking themselves. With the expansion of mutual index and ETF products — covering an array of assets and geographies — shifting cash into diversified trackers is simple. Investment apps allow it to be done with the flick of a finger. For households seeking to earn more from their savings, the growth of these low-cost investment vehicles is an unalloyed good.
Seeking out star or dud stocks is a costlier, more research-intensive exercise, and necessitates a higher fee-based business model. Poor long-term performance and the allure of cheaper passive strategies — which account for 40 per cent of the $45tn worldwide fund assets tracked by Morningstar, up from 14 per cent in 2008 — have eroded active managers’ inflows. Many are cutting costs and restructuring. In its annual results this week, Edinburgh-based Abrdn committed to axing 500 jobs amid large outflows.
The industry and some economists worry that the continued flow of money into buy and hold funds could harm financial markets. Beyond a certain threshold, they argue, a lack of active traders engaged in weeding out over- or underpriced companies could lead to a greater misallocation of investors’ cash.
For now this is just a theoretical concern. In practice, active managers still dominate the global industry. Finding alpha may be hard, particularly when markets are dominated by a few stocks, but opportunities have not suddenly disappeared. And big institutional investors, such as pension funds, still want to put their cash piles to work. Indeed, there remains plenty of interest in market-beating trades. For measure, hedge funds — which deploy higher-risk active strategies for accredited investors — currently outnumber Burger King outlets across the globe.
This is a cut-throat industry. Active funds are competing with hard-to-beat passive strategies, and they are engaged in a zero-sum game with other active players. For each punt, there is a loser taking the other side of the bet. According to Morningstar, in the year to June 2023, 27 per cent of actively managed global large-cap equity funds beat the equivalent passive fund. Over a 15-year timeframe, only 3 per cent have. Active traders can hardly blame investors for switching to index strategies. To survive, they must prove they can actually make money.
Slashing fees, by cutting business costs, is one option to boost the odds of making market-beating returns. Some funds have also found greater chances of beating benchmarks in bond markets and more niche corners of the stock market. Others, like Citadel or DE Shaw, have hired the brightest quant minds or tried deploying tech — from AI to high-frequency trading — to find alpha. Today’s economic uncertainty and the potential for higher-for-longer interest rates should create the volatility that hawk-eyed traders can thrive on.
Yet investors are unlikely to diverge from Bogle’s safe and sound advice without a good reason. That means if the stock pickers are to survive and thrive, they will have to work even harder to offer them one.